Every business needs an HR department to draft policies and procedures. HR policies form a solid foundation for managing the company and staff, ensuring the development and safety of the employees. Drafting HR policies for a private limited company is essential to prevent legal compliance issues. These policies also create a sense of employee accountability and help maintain proper conduct in the workplace. HR policies define individual rights, obligations, and behaviour towards their co-workers.
This blog explains what a human resource policy is, its types and elements.
What are HR Policies?
HR policies are guidelines and rules that govern employee behaviour, practices, and interactions within an organisation. These policies safeguard both the employer and the employees. For employers, policies establish a framework for consistent decision-making and legal compliance while clarifying employee expectations, benefits, and procedures.
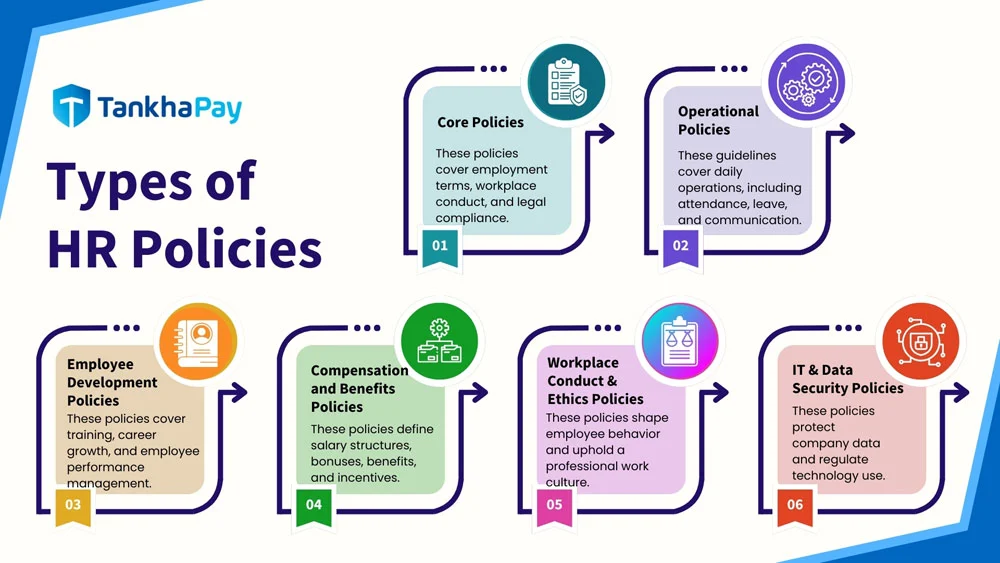
Types of HR Policies
The different types of human resource policies are as follows:
- Core Policies: These fundamental policies address basic employment terms, workplace conduct, and compliance with legal regulations.
- Operational Policies: They are specific guidelines for daily operations, covering areas like attendance, leave, and communication.
- Employee Development Policies: These policies focus on training, career development, and performance management of employees.
- Compensation and Benefits Policies: They outline the organisation’s approach to salary structures, bonuses, benefits, and incentives.
- Workplace Conduct & Ethics Policies: These policies guide employee behavior and maintain a professional work culture.
- IT & Data Security Policies: These policies protect company data and regulate technology use.
Key Elements of HR Policies
The elements of HR policies are as follows:
- Effective HR policies are clear, concise, and written in a language easily understood by all employees.
- HR policies must adhere to laws to protect the organisation and its employees from legal complications.
- Policies should be flexible to accommodate changes in the business environment, industry standards, and emerging trends.
- HR policies should be easily accessible to all employees, and any updates or changes should be communicated promptly.
HR Policies in India
Companies must comprehensively understand the laws and regulations that govern HR administration in a particular country. This is especially significant in India, where federal, state, and industry-specific regulations oversee labour laws. The human resource policies that companies commonly practice are as follows:
Organisations must provide employees with meals, rest, and lactation breaks to comply with the law. A clear policy outlining the rules and restrictions is necessary to meet these needs.
A timekeeping policy emphasises the importance of accurately tracking work hours and proper procedures for recording them. A payday policy includes essential details about compensation, such as payday protocols on holidays, pay methods, and frequency of paydays.
Employees often use their own devices for work purposes. To ensure security, consider setting limitations and security requirements.
Draft a policy addressing the organisation’s stance on drug and alcohol use, considering state laws. Specifying prohibited substances, testing procedures, and disciplinary actions for violations is crucial in safety-sensitive industries like construction.
Explain the company’s stance on remote work and list the policies for telecommuting. This includes eligibility for remote employment, limitations for remote roles, monitoring remote employees, pay and time policies, and the organisation’s right to terminate telecommuting at any time.
An at-will employment policy emphasises that the employee or organisation can terminate the working relationship for any lawful reason and at any time.
Include a social media policy in employee handbooks to safeguard the company’s online reputation. Specify prohibited topics or information on social media, outlining disciplinary actions for violations.
Companies should establish employee guidelines for behaviour, professionalism, and ethics. This helps in promoting and maintaining a healthy working environment. The code of conduct usually includes equal rights, technology usage, conflict of interest, media policy, and dress code.
These policies ensure all employees have equal opportunity by prohibiting discrimination based on gender, religion, caste, disability or age. They help promote diversity in recruitment, training, promotion and compensation practices.
Company HR policy should describe paid and unpaid leaves. Paid leaves include sick leaves, casual leaves, national and public holidays, and maternity and paternity leaves. Establish the procedures for requesting and approving leaves, maintenance of attendance records, and addressing any leave-related queries.
Establish a system for employees to report concerns without fear of retaliation. Make a framework for investigation procedures and redressal.
Performance management involves goal-setting, evaluation, feedback, and development plans. Establish clear criteria and reliable methodologies to conduct fair and objective performance appraisals.
Create policies and procedures to prohibit, prevent, address, and redress incidents of sexual harassment in the organisation. Ensure the policy complies with the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition, and Redressal) Act of 2013.
Set up rules to ensure workplace safety, accident reporting, emergency protocol, and promotion of employee well-being. The policy should comply with the Occupational Safety and Health Act and relevant regulations.
Establish clear guidelines for the appropriate use of IT resources, including email, internet access, and software. Ensure data security, privacy compliance, and data protection protocols are in place.
Policies should detail working hours, overtime benefits, and lateness penalties. The new labour code limits the daily operating hours to 12, with a maximum of 48 hours per week. Employees may be eligible for a 4-day workweek. Overtime working hours have been raised to 125 hours across all industries.
Define the rules of interpersonal relationships between employers and employees, including roles and responsibilities. This ensures accountability of those in supervisory positions for their impact on other employees during and after office hours.
A comprehensive employment contract covers probation, assessment procedures, eligibility for permanent employment, and termination rules. Proper documentation helps navigate the complex employment framework and assists HR in managing employee termination or resignation.
Companies must comply with the Employees’ Provident Fund Act of 1947 by setting up provident fund accounts for each employee. Businesses with over ten employees must pay provident funds and gratuities to eligible employees who have worked for five years straight, per the Payment of Gratuity Act of 1972.
Companies must include a clause in the employee contract if they require employees to sign an NDA. Once the employee signs the NDA, they must comply with its terms and refrain from sharing confidential information about the business practices with anyone. Should an employee breach the NDA, they may face severe consequences as a result.
Functions of HR Policies
Some functions of HR policies are as follows:
- Outline the opportunities for career growth in an organisation.
- Help foster a healthy working environment.
- Ensure the organisation stays legally compliant.
- Provide guidelines for supervisors and managers.
- Create a basis for the employee handbook.
- Set the foundation for accountability during the decision-making process.
- Ensure the proper application of policies at every level of the company.
Benefits of HR Policies
Human resource policies have the following benefits:
- Decision-Making: Policies provide a clear basis for decisions, allowing executives to address HR issues confidently.
- Effective HRM: Framed policies eliminate confusion, ensuring a more effective and streamlined human resource management process.
- Prevent Discrimination: Policies discourage discrimination, requiring consistent and standard behaviour towards all employees.
- Restrain Injustice: Policies limit discretionary decisions and prevent biased management from making unfavourable choices.
- Decentralisation of Authority: HR policies contribute to decentralisation by delegating authority to lower-level staff, easing the workload for senior management.
- Time Savings: Guidelines provided by HR policies eliminate the need for individual analysis and discussions, saving time in addressing problems.
- Continuity and Uniformity: Policies facilitate smooth transitions when managerial changes occur by ensuring continuity and uniformity.
How to Formulate HR Policies
You can formulate HR policies by following these steps:
Identify the Need
Organisations need HR policies in hiring, training, compensation, and industrial relations. The HR manager should convince the Chief Executive to implement policies if they still need to be put into place. Existing policies may need revision, which can be suggested by staff experts, union leaders, supervisors, or employees.
Accumulating Information
Collect the necessary facts. This can be done by a committee or specialist within or outside the organisation. The information can be gathered from various sources, such as earlier and current practices, management attitudes, experiences, and knowledge. The HR department can study existing documents, survey industry practices, and interview people within the organisation. Extensive consultations and discussions should be conducted to ensure the policies are helpful later.
Examining Alternative Policies
Evaluate the alternatives based on the data collected. Secure the active participation of those who must follow the policies.
Put the Policy in Writing
Start writing the HR policy after gathering information and examining alternatives. Avoid emotional phrasing while writing the policy.
Getting Approval
Send the draft to higher management to get approval. Only higher management has the authority to make the final decision on whether a policy adequately represents the organisation’s objectives or not.
Communicate the Policy
After receiving the approval of top management, the policy should be communicated to the rest of the organisation. Create an education program for personnel issues based on the new policy.
Evaluate the Policy
Policies should be evaluated over time based on practical experience. If an organisation is not seeing the expected results, modifications may be required. Serious issues should be reported to top management to decide on policy re-statement or reformulation.
Best Practices in HR Policy Formulation and Implementation
The best practices are as follows:
- Involve key stakeholders, including employees, in the policy development process for a diverse range of perspectives.
- Policies should be regularly reviewed and updated to align with evolving business needs, industry standards, and legal requirements.
- Training programs and regular communication channels ensure employees are educated about the policies.
- Consult legal experts to ensure HR policies comply with existing laws and regulations.
- Establish a feedback mechanism for employees to provide policy input and report any concerns or ambiguities.
Factors Affecting HR Policies
The major factors affecting human resource policies are as follows:
- Company Business Policy: HR policy must align with business goals to effectively manage the organisational structure and employee competencies. This can be challenging, particularly with a larger workforce and diverse skill sets.
- Social Factors: HR policies need to consider social forces and their impact on the supply of a skilled workforce. Incentives that work in other countries may not align with employees’ cultural beliefs and values. A diverse workforce can challenge the implementation of an individual-oriented performance management system.
- Regulations: HR managers must be well-versed with labour regulations when designing policies. Laws protect workers from hardship. HR policies should consider the regulations to avoid labour queries, interventions, and damage to reputation.
- Advancing Technology: Technology affects HR policies and practices. Companies should consider emerging technologies when designing HR policies to avoid higher operating costs than competitors.
- Competition and Competitor Behaviour: HR policies should consider labour market conditions and competitors’ practices. The company must adopt a flexible approach to motivate employees in a tight market. In a low-demand market, employees must accept harsh employment conditions. Competitors’ practices offer learning opportunities.
- Internal HR Environment: Effective HR policies consider internal factors like employee beliefs, organisational structure, and external factors.
HR Forms
HR forms help an organisation track information and establish agreements with the staff. Some of these forms are as follows:
- Business Expenses: These forms help employees track and request reimbursement for business-related expenses, especially during work-related travel. Separate forms may be used for supplies or inventory needs.
- Performance and Discipline: Key events such as performance improvement plans, oral and written warnings, promotions, recognitions, and performance reviews are documented in this form.
- Reasonable Accommodation Requests: The government mandates that employers offer reasonable accommodations for religious beliefs or disabilities. This form maintains detailed records of all communications related to reasonable accommodation requests.
- Leave of Absence: Most organisations require a written request for time off to keep track of things like vacation days.
- Employee Handbook Agreements: This form requires employees to read, understand, and comply with all company policies.
- Hiring Forms: Organisations utilise forms in the hiring process to identify and onboard quality candidates. After hiring, candidates must fill out any mandatory government forms.
- Receipt of Company Property: This form documents company-supplied items like tools or equipment issued to employees. Tracking company property helps ensure items are returned, and similar forms may be used when employees leave.
Conclusion
HR policies are crucial for a positive workplace culture and smooth operations. By understanding and embracing best practices, businesses can create an environment where employees thrive. As the business landscape evolves, HR policies must adapt while remaining committed to fairness, transparency, and compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an SOP for HR policies?
SOPs provide HR teams with instructions for attracting and retaining new talent, managing employee performance, and implementing company-wide policies at scale.
Why does an organisation need HR policies?
HR policies provide a structured framework for managing human resources, ensuring consistency in legal compliance, and fostering a positive workplace culture.
How often should HR policies be reviewed and updated?
HR policies should be reviewed regularly, ideally annually, to ensure they align with legal requirements, industry standards, and the organisation's evolving needs. Updates should be made as needed.
What is the role of HR policies in legal compliance?
HR policies ensure legal compliance by providing guidelines that adhere to employment laws and regulations. They help mitigate legal risks and protect the organisation from potential lawsuits.
Can HR policies be changed without notice?
HR policies should not be changed without notice. Changes should be communicated to employees, allowing them to understand and adapt to the modifications.
Also Read
- Payroll Process – Basics, Requirements, Compliances
- What is Payroll Management System? – Definition and Importance