Form 16 and Form 12BA are essential documents for salaried individuals. Form 12BA is an annexure to Form 16. It provides details about the valuation of perks given to the employee, the amount recovered (if any) from the employee, and the taxable value of the perquisite, as per the prescribed format.
Let’s discuss Form 12BA–its purpose, format, and applicability per the Income Tax Act.
What is Form 12BA?
Form 12BA is a statement that an employer issues to their employee. The statement details the perquisites, fringe benefits, and profits an employee receives instead of their salary. This form is necessary to accurately assess tax payments as it covers all the non-monetary benefits an employee receives. By providing a personalised breakdown of the various factors that constitute total salary, the form helps determine the tax liability.
What are Prerequisites?
Employees often receive additional perks in addition to their salary. Perks, also known as prerequisites, are the benefits of a job or position. Perks can be either monetary or non-monetary.
Monetary perks are cash payments made by the employer on behalf of the employee or reimbursements for certain expenses, such as education, medical bills, gas bills, helper salaries, electricity bills, vacation expenses, etc.
Non-monetary perks are benefits given in kind. For example, an employer may offer rent-free accommodation or accommodation at a concessional rate, employee stock options (ESOPs), restricted stock units (RSUs), or contributions to an approved superannuation fund.
The income tax laws specify the rules for valuing various types of perks. Employers must provide a separate statement detailing the various perks given to employees, which should be filled out in Form No. 12BA.
Applicability of Form 12BA
Form 12BA is a document provided explicitly for the declaration of perquisites received by an employee, separate from the information already contained in Part B of Form 16. Its issuance is mandated only when an employee’s salary exceeds Rs 1,50,000. In cases where the salary falls below this threshold, the details of perquisites included in Part B of Form 16 are deemed sufficient, obviating the need for Form 12BA.
For clarity, ‘salary’ encompasses pay, allowances, bonuses, commissions, or any monetary payment from one or more employers. Notably excluded from this definition are dearness allowances, employer contributions to provident funds, exempt allowances, and various other payments specifically excluded from being considered perquisites. Lump-sum payments received upon termination of service or retirement, such as gratuity or leave encashment, also fall outside the scope of ‘salary’ for this purpose.
It’s crucial to note that Form 12BA must be issued irrespective of whether the employee has received any perquisites. In cases where no perquisites have been received, the employer must explicitly state so on Form 12BA. This ensures comprehensive reporting and compliance with tax regulations.
When is Form 12BA Required to be Issued by the Employer?
Form 12BA is a document that needs to be provided when an individual’s salary exceeds Rs. 1,50,000.
Salary includes various components such as:
- Basic Pay
- Bonus
- Commission
- Allowances
- Any other monetary payment
However, there are specific components that are excluded from salary, such as:
- Dearness Allowance
- Exempt Allowances
- Employer contribution to PF
- Value of perquisites under section 17(2)
- Payments that are not part of the perquisites
- Superannuation
- Voluntary retirement benefits
- Commutation of pension
- Lump-sum payment for cessation of service.
Purpose of Form 12BA
The income under the salary head is comprised of three components:
- Salary
- Perquisites
- Profits instead of salary
Perquisites, or perks, are additional benefits that employees receive in addition to their salary. These benefits can be monetary or non-monetary, such as education expenses, driver salary, rent-free accommodation, stock options, and medical expenses.
The income tax rules govern the calculation of the taxable value of each perk, and the employer deducts the tax. The taxation treatment of perks can be complicated, so the income tax rules mandate employers to provide a separate form to employees, along with Form 16, to help them understand their tax deductions.
Who Issues Form 12BA, and When?
Employers must issue Form 12BA and Form 16 by 15th June of the following financial year.
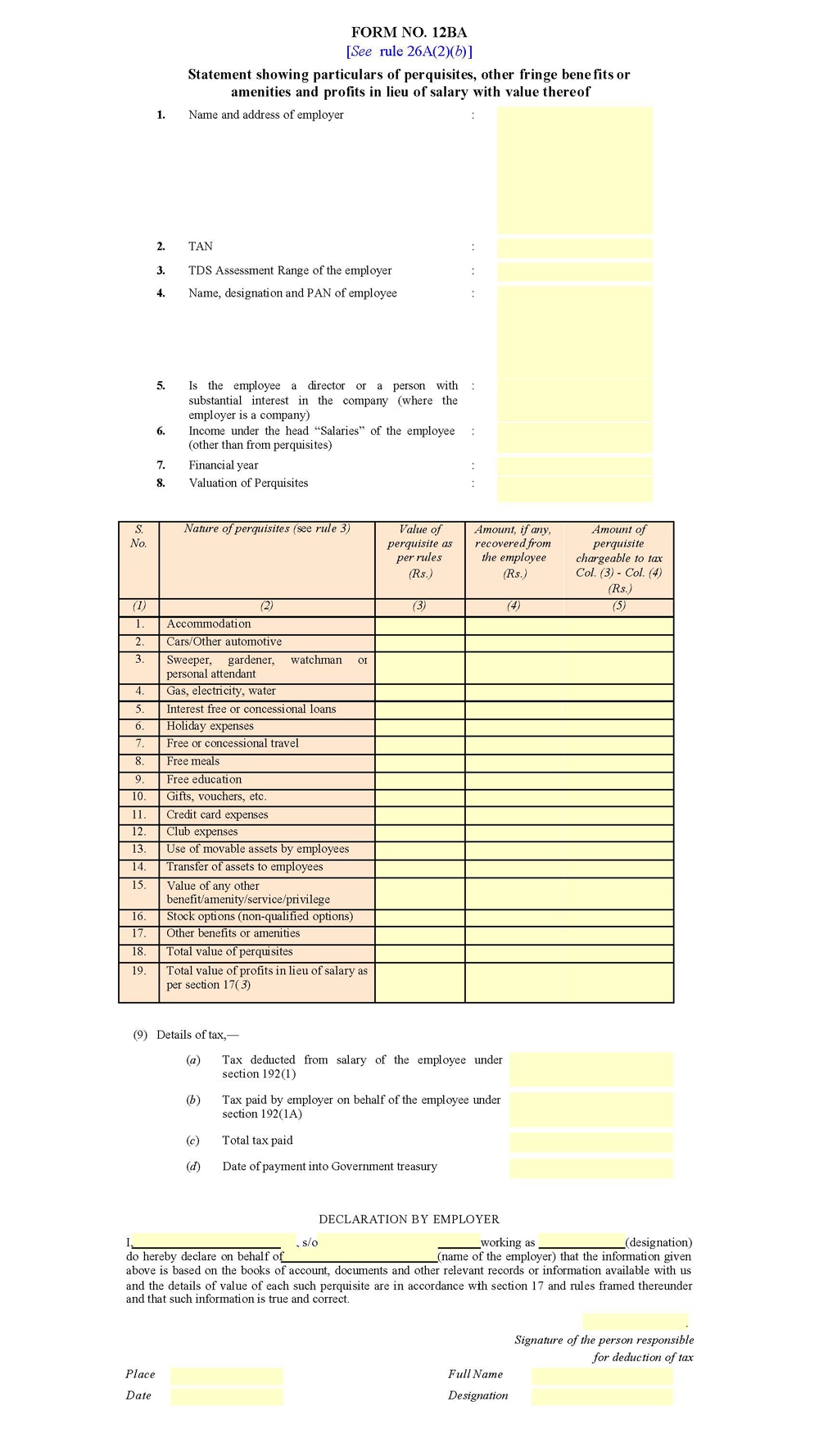
Form 12BA Format
The Form 12BA has four sections that need to be filled out.
Employer Details Section
The first section requires details about the employer and employee. The Employer Details section needs the employer’s name, address, and TAN. The Assessing Officer Code of the employer is specified in Form 12BA, unlike in Form 16, where the Assessing Officer Code is associated with the PAN number. This section requires the employee’s name, designation, PAN number, and financial year.
Value of Perquisites Section
The Value of Perquisites section calculates the perquisites and their taxable amount. The section has three columns that include the amount as per the rules, the amount recovered from the employee, and the amount of taxable perquisites.
Details of Tax Section
The Details of Tax section is based on Form 16, and all the necessary details should be available. This section provides more clarity on the tax details.
Declaration from the Employer Section
The Declaration from the Employer section needs to be filled out by the employer. The details here are for the declaration of the person responsible for the information provided in the form.
Form 12BA Sample
How to Fill Form 12BA
Form 12BA is a statement that employers give to their employees regarding prerequisites provided by the employer. It contains details such as the value of perquisites, profits in place of salary, etc.
Part A – Employer Details:
- Input the employer’s name and complete address.
- Specify the employer’s Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number (TAN).
Part B – Employee Details:
- Provide the employee’s name and residential address.
- Include the Permanent Account Number (PAN) of the employee.
Part C – Salary and Other Income Details:
- Detail the salary paid to the employee, along with any other allowances.
- Include information regarding perquisites, profits in place of pay, and similar benefits.
- Specify particulars regarding rent-free accommodation, provision of a motor car, or any other movable assets granted to the employee.
Part D – Other Information:
- Provide any relevant information necessary to ensure accurate reporting and add it to the form.
Declaration:
- The employer must sign and date the declaration, confirming accuracy.
Verification:
- The employer must sign the verification section, including their designation and date of signing.
Difference Between Form 12BA and Form12 B
It is important to note that Form 12BA and Form 12B have distinct purposes in income tax documentation despite their similar names.
Form 12B is typically required when an individual changes jobs during a financial year, and their income details must be collected for both the previous and current employment. This form ensures a smooth transfer of information between the previous and new employers.
On the other hand, Form 12BA focuses on the perks, facilities, and fringe benefits that an employer provides to their employees. This form considers the additional benefits beyond the wage agreement. It can be regarded as an individual’s income and lifestyle for tax purposes.
Form 12B deals with employment changes, while Form 12BA provides information on non-wage benefits and enhancements an employer offers.
Difference Between Form 12BA and Form12 BB
Form 12BA and Form 12BB are essential documents that serve distinct purposes in income tax documentation.
Form 12BA is a document that the employer furnishes to the employee. It contains details about the perquisites and other allowances provided to the employee throughout the financial year. It helps the employee during income tax filing. Form 12BA accurately determines their tax liability when shared promptly by incorporating all relevant income components.
On the other hand, Form 12BB is a statement that the employee submits to the employer. It outlines the investments made and claims availed by the employee during the financial year. This form provides crucial information for tax calculation purposes, allowing the employer to consider eligible deductions and exemptions while computing the employee’s tax liability.
Form 12BA helps employees understand their income components. At the same time, Form 12BB enables employers to factor in investment declarations and claims for accurate tax calculation. Both forms ensure precise tax assessment and compliance when submitted timely.
Frequently Asked Questions
Form 12BA Applicability
Taxation on income has the details of Form 16. However, Form 12BA adds to the details of Perquisites provided by the employer to the employee. However, it is crucial to understand that Form 12BA applies to any employee regardless of whether they receive any perquisites.
What is form 12BA in salary?
Form 12BA is a statement for income tax that provides details of perquisites, amenities, fringe benefits, and profits in lieu of salary offered by the employer.
Are Form 12B and 12BA the same?
Form 12BA is a statement that an employer must provide to employees outlining their benefits. On the other hand, Form 12B is a statement that an employee must furnish to a new employer if hired over the fiscal year.
What is the purpose of Form 12BA?
Form 12BA is an income tax statement outlining an employer's compensation, perks, and benefits, including fringe benefits and profit instead of salary. It details the value of these payments and the recipient's tax liability to the government.
Is it mandatory for the employer to issue Form 12BA?
Yes, if the salary exceeds Rs. 1,50,000.
If the value of perquisites is nil, is Form 12BA required to be issued?
Form 12BA must be issued even if the value of perquisites and benefits is nil, provided the salary exceeds Rs. 1,50,000.
Are Form 16 and Form 12BA the same?
Form 12BA is an annexure to Form 16. Form 12BA contains details of the value of perks, and Form 16 details the entire salary breakdown, tax deduction, and deposition details with the government.