Advance tax payment is a system where taxpayers can spread their tax obligations by making payments in multiple instalments throughout the fiscal year rather than settling the entire amount in one go. It is often considered a tax EMI. This method reduces immediate financial burdens and streamlines filing for income tax returns (ITR). This article covers everything about Advance Tax- from the basics, like its definition and payees, to the nitty-gritty in the form of rules and regulations. Read on to discover more.
What is Advance Tax?
Advance tax is the income tax a taxpayer pays in advance instead of making a lump sum payment at the end of a fiscal year. It is a tax that an individual pays as they earn. An individual can pay the tax amount in instalments per the due dates given by the Income Tax Department.
Who pays Advance Tax?
Advance Tax is paid when:
- If the total tax liability of an individual is more than Rs. 10,000 in a fiscal year, advance tax has to be paid. Advance tax applies to all taxpayers, salaried employees, freelancers, and businesses.
- Taxpayers opting for the presumptive scheme under section 44AD must make a single instalment payment for their advance tax by March 15. They also have the option to settle all their tax obligations by March 31.
- Professionals like doctors, lawyers, architects, and others fall under the presumptive scheme per section 44ADA. They must clear their entire advance tax obligation in a single instalment by March 15. They can also settle the total amount by March 31.
- Non-resident individuals and foreign corporations that generate income in India must obey advance tax obligations when their tax liability exceeds Rs. 10,000.
- Certain businesses, like lottery and horse racing, must pay advance tax on specified incomes, regardless of whether they exceed Rs. 10,000.
- Individuals who only earn salary income and do not have any additional income sources are generally not liable to pay advance tax.
- Only senior citizens (60 years or older) with business income must pay advance tax.
Advance Tax Due Dates For FY 2023-24
The due date to pay the final instalment for advance tax for Financial Year 2023-24 is March 15, 2024. Taxpayers have to pay 100% of their tax liability by this date.
Advance Tax Payment for Companies
| Due Date of Tax Instalments | Amount of Tax Payable |
|---|---|
| On or before June 15, 2023 | 15% |
| On or before September 15, 2023 | 45% |
| On or before December 15, 2023 | 75% |
| On or before March 15, 2024 | 100% |
Advance Tax Payment for Business Owners and Self-employed
| Due Date of Tax Instalment | Amount of Tax Payable |
|---|---|
| On or before September 15, 2023 | 30% |
| On or before December 15, 2023 | 60% |
| On or before March 15, 2024 | 100% |
Advance Tax Payment for Businesses and Professionals opting for presumptive taxation scheme under Section 44AD/44ADA
| Due Date | Amount of advance tax |
|---|---|
| On or before March 15, 2024 | 100% of advance tax |
Advance Tax Calculation
You can calculate advance tax by following the steps given below:
- When determining your advance tax calculations, calculate the total income from all sources received between April 1 and March 31 for the relevant financial year.
- Make all eligible deductions and exemptions.
- Calculate the tax payable by applying the income tax slab applicable to you.
- Decrease the tax amount deducted through TDS/TCS.
After calculating your advance tax liability (if the amount is more than Rs. 10000), you can pay advance tax in instalments, as discussed in the previous section.
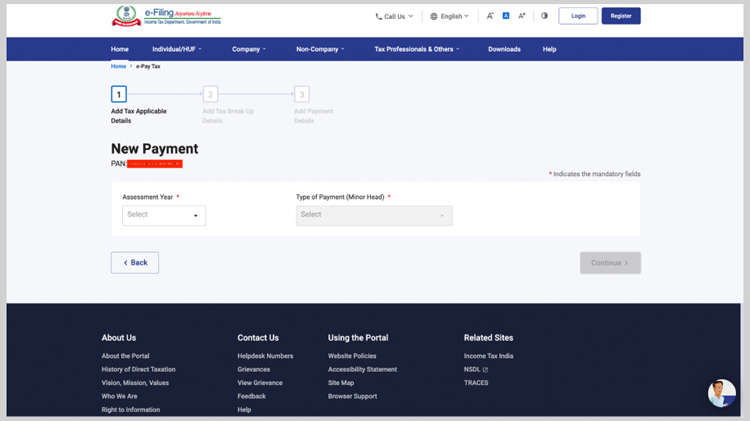
How to pay Advance Tax online?
Advance Tax can be paid online through the online facility of the Income Tax department. The following steps can help you make a payment for advance tax online:
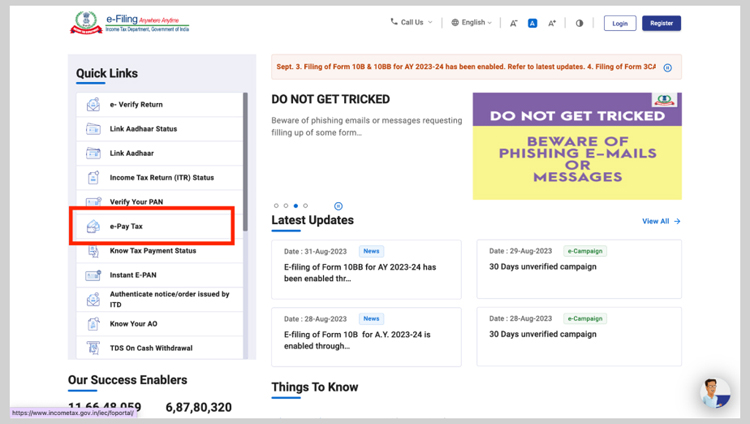
- Visit the official website of the Income Tax Department of India click here.
- Click on the ‘e-pay’ option tax on the left side under ‘Quick Links’.
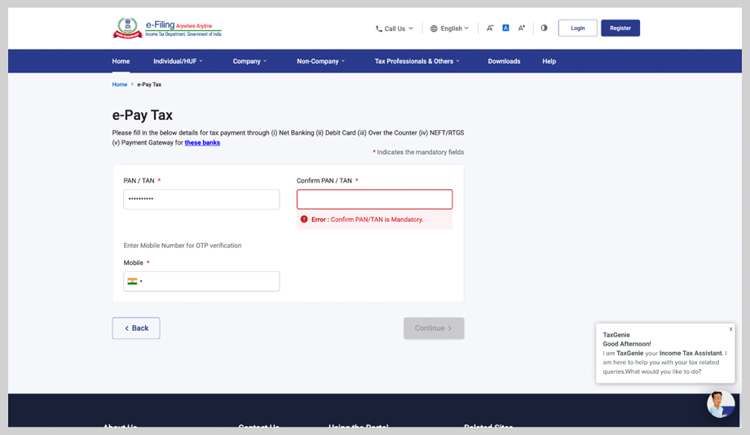
- Enter your ‘PAN’ and ‘Mobile Number’.
- Enter the ‘OTP’ you receive on your mobile and click ‘Continue’.
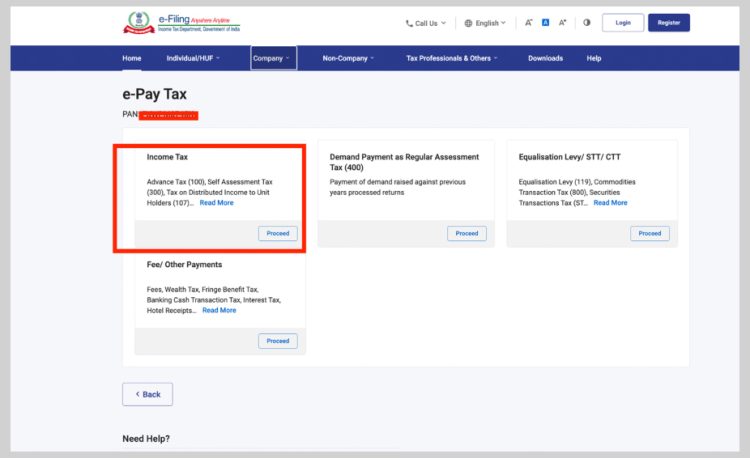
- Select the ‘Income Tax’ option and click ‘Proceed’.
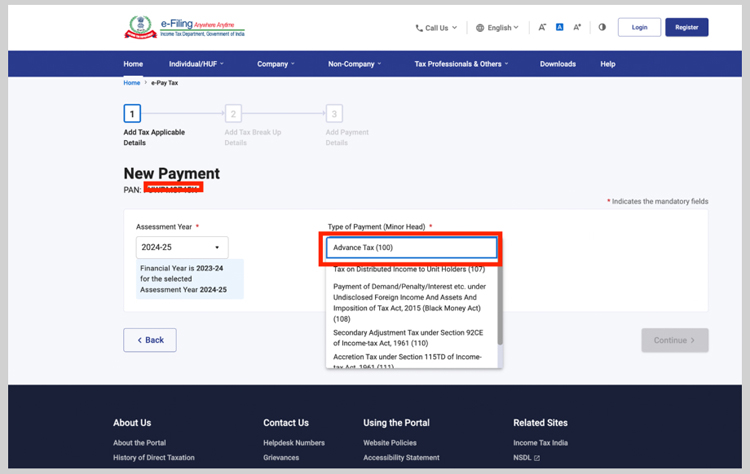
- Select the Assessment Year for which you want to pay advance tax, select the payment type as advance tax from various options, then click ‘Continue’.
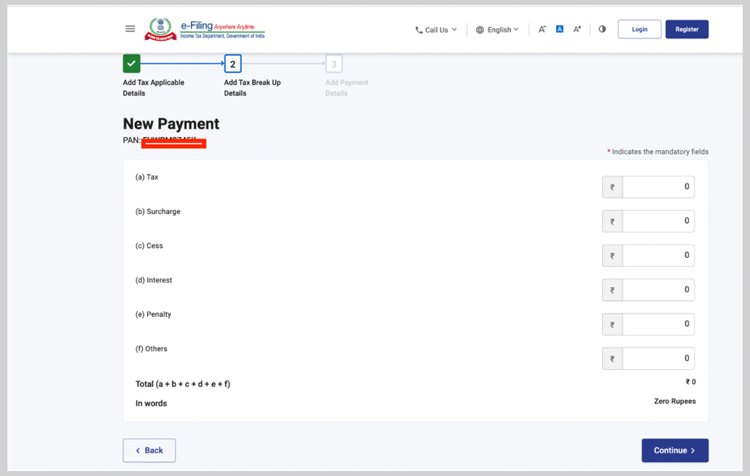
- Feed the amount of tax to be paid in the tax category and click ‘Continue’.
- After payment, you will get a challan for your reference and ITR Filing.
Advance Tax Late Payment Interest
Taxpayers should make advance tax payments within the four deadlines of that fiscal year. If the advance tax payment is not timely, then interest is liable to be paid.
- Non-payment of advance tax attracts interest under 234B: According to Section 234B, paying a minimum of 90% of total tax liability as advance tax by March 31 is essential—failure to make payments results in a charge of 1% interest on the unpaid amount.
- Late payment of advance tax attracts interest under 234C:
| Particulars | Rate of Interest | Period of Interest | Amount on which Interest is Calculated |
|---|---|---|---|
| If Advance Tax paid on or before June 15 is less than 15% | 1% per month | Three months | 15% of Amount ( – ) tax paid before June 15 |
| If Advance Tax paid on or before September 15 is less than 45% | 1% per month | Three months | 45% of Amount ( – ) tax paid before September 15 |
| If Advance Tax paid on or before December 15 is less than 75% | 1% per month | Three months | 75% of Amount ( – ) tax paid before December 15 |
| If Advance Tax paid on or before March 15 is less than 100% | 1% per month | One month | 100% of Amount ( – ) tax paid before March 15 |
Exemptions under Advance Tax
The exemptions under advance tax are as follows:
- Senior citizens aged 60 years and above are exempt from paying the advance tax.
- Salaried individuals who fall under the TDS net are exempt from paying the advance tax. However, earnings from income sources such as interest, capital gains, and rent will attract advance tax.
- If the TDS deducted is more than the tax payable for the year, then you do not have to pay the advance tax.
Benefits of paying Advance Tax
The benefits of paying advance tax are as follows:
- When taxpayers pay their taxes in advance, they can avoid concerns about monetary shortages or scrambling for last-minute tax payments.
- It helps speed up the collection of taxes.
- Advance tax payment saves people from defaulting on their tax payments.
- It aids businesses in effectively managing their finances and offers insight into their income for the year.
- The government can earn an interest on the collected amount, increasing government funds.
Refund on Advance Tax
You can get a refund on advance tax payment for the following reasons:
- At the end of the year, if the Income Tax Department finds out you have paid more tax than you should have, it will refund the excess amount.
- Taxpayers can claim a refund by submitting Form 30. They have to claim within one year from the last year of the assessment year.
Advance Tax Challan 280
Challan 280 allows people to pay income tax online on the website of the Income Tax Department of India. On the website, people must select this challan, fill out the form and then use it to pay taxes online/in the office. The prerequisites of Challan 280 are as follows:
- PAN Details: It is essential to provide the correct PAN details. Failure to do so risks your tax being deposited in someone else’s name.
- Assessment Year: Choose the valid assessment years for which you will pay your tax because the tax is going out in advance for the following fiscal year.
- Selecting the Payment Type: The taxpayer must choose the payment type in the form. If you pay for the same financial year based on estimated income, it will be advance tax. On the other hand, if you pay after the completion of the financial year, it is considered a self-assessment tax.
Example of Advance Tax
Jyoti works in a company and also works as a freelancer. Her earnings from her salary are Rs. 10 lakh before providing the benefit of any deductions or exemptions. Her net receipts (after giving the use of expenses) from her freelance work are around Rs.10 lakh. She is investing Rs. 1.5 lakh in PPF and paying Rs. 25,000 as her medical insurance. She is also getting Rs. 15,000 as interest on her fixed deposits. Her employer has deducted a TDS of Rs. 1,00,000 from her salary. So, the final calculation and advance tax liability are as follows:
| Income Estimate | Amount In Rs. | Amount In Rs. |
|---|---|---|
| Income from Salary: | ||
| Income | 10,00,000 | |
| Less: Standard deduction | 50,000 | |
| Income from Salary: | 9,50,000 | |
| Income from Profession: | 10,00,000 | |
| Income from other source: | 15,000 | |
| Gross Total Income | 19,65,000 | |
| Deductions under Chapter VIA | ||
| 80C: | 1,50,000 | |
| 80D: | 25,000 | |
| Total Deductions | 1,75,000 | |
| Total Income | 17,90,000 | |
| Tax Payable as per OLD Regime | 3,49,500 | |
| Education cess | 13,980 | |
| Total tax Liability | 3,63,480 | |
| TDS deducted | 1,00,000 | |
| Tax Payable as advance Tax | 2,63,480 |
| Due date | Advance Tax Payable | Advance tax |
|---|---|---|
| June 15 | 15% of advance tax liability | 39,522 |
| September 15 | 45% of Advance tax liability | 79,044 |
| December 15 | 75% of Advance Tax Liability | 79,044 |
| March 15 | 100% of Advance Tax Liability | 65,870 |
Conclusion
Understanding and proactively managing advance tax obligations can pave the way for individuals and businesses financial stability and peace of mind. By spreading tax liabilities across the fiscal year, taxpayers can mitigate the strain of hefty lump-sum tax payments, ensuring smoother cash flow and better financial planning.
Furthermore, advance tax calculations offer invaluable insights. They facilitate informed decision-making and provide a comprehensive view of earnings and financial health. Whether you’re a freelancer, a professional, or a business owner, embracing the principles of advance tax can be a game-changer.
While advance tax might seem daunting at first glance, it is a testament to prudent financial planning and responsible citizenship. With this knowledge, you’re better equipped to confidently navigate the tax landscape, ensuring compliance and financial well-being.
Remember, knowledge isn’t just power in taxation—it’s peace of mind. Here’s to making informed decisions, optimising resources, and embracing the journey towards fiscal responsibility with assurance.
Frequently Asked Questions on Advance Tax
Is an NRI responsible for the payment of advance tax?
An NRI with an income in India over Rs 10,000 is liable for the payment of advance tax.
Should I pay advance tax as a senior citizen with a pension and interest income?
Senior citizens without an income from businesses or professions are not liable for advance tax.
Will I be penalised if I do not pay advance tax?
Non-payment of advance tax will result in an interest under Sections 234B and 234C of the Income Tax Act of 1961.
Can I claim a deduction under Section 80C while estimating income to determine advance tax?
You can consider all these deductions while calculating your income for the year to compute your advance tax liability.
What happens if I miss the deadline to pay the fourth instalment of my advance tax?
You can still proceed with the payment of advance tax on or before March 31 of the year, and such payment will still be treated as advance tax only.
Which challan is used for the payment of advance tax?
Challan 280 is the challan required to pay for advance tax payment.
How do you make advance tax payment?
Challan 280 is used, like any other regular tax payment, to make advance tax payment.
What happens if advance tax paid exceeds total tax liability?
The extra amount will be returned if the advance tax payment exceeds the total tax liability. If the amount is more than 10% of the tax liability, then the Income Tax Department will pay an interest of 6%.
What is the mode of payment of advance tax?
You can pay your advance tax by internet banking or through challan.
What is the due date for the payment of advance tax?
June 15, September 15, December 15 and March 15 are the due dates for advance tax payments. The entire tax liability should be paid by March 15.
How to pay advance tax for capital gains?
You must pay the advance tax on Capital gains. However, it is impossible to predict the amount of capital gain in advance accurately. Therefore, if you earn capital gains after the due date, you can pay the advance tax in the remaining instalments.
For what period is an individual's income considered when calculating advance tax?
Income earned in the twelve months between April 1 to March 31 (commonly called a Financial Year) is considered for calculating advance tax.